Exploring Organoid Intelligence: A New Frontier in AI
Written on
Chapter 1: The Rise of Organoid Intelligence
Organoid intelligence (OI) presents an intriguing alternative to traditional artificial intelligence (AI). This concept revolves around cultivating miniature brains in laboratories and training them to carry out specific tasks. We will delve into the current landscape of organoid intelligence, examining its capabilities and limitations along with the ethical considerations it raises.
Artificial intelligence has emerged as one of the most significant technological advancements of the 21st century, permeating various sectors including healthcare, finance, and entertainment. Nevertheless, existing AI systems primarily depend on artificial neural networks that, while inspired by the human brain, differ fundamentally from biological neurons. Consequently, these AI systems encounter challenges in adapting to new situations and generalizing knowledge, which can hinder their effectiveness.
Section 1.1: Understanding Organoids
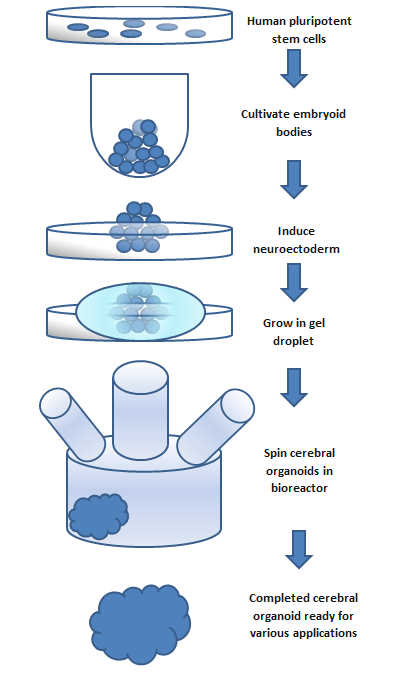
Organoids are three-dimensional structures derived from stem cells, designed to replicate the complexity of various organs, such as the brain and liver. The process begins by isolating stem cells from a tissue sample—be it skin or blood—which are then cultured in a specific medium that encourages differentiation into the desired cell types.
Organoids have gained traction in biomedical research as a valuable tool for investigating human diseases in a controlled setting. For instance, scientists have utilized brain organoids to explore conditions like autism and schizophrenia, which are challenging to model with animal studies.
Subsection 1.1.1: The Mechanism of Organoid Intelligence

A fresh perspective in AI, organoid intelligence focuses on developing intelligent systems by mimicking human brain structure and function. The initial phase involves cultivating a brain organoid in a lab, which is subsequently linked to a computer. This setup allows for the exchange of signals, enabling the organoid to learn to interpret and react to these signals in alignment with its training.
The unique advantage of OI over conventional AI lies in its learning methodology. Similar to human learning, which builds upon prior experiences, OI systems can adapt based on past interactions, offering a more organic approach to learning.
Section 1.2: Potential Applications of Organoid Intelligence
The applications of OI are vast, spanning numerous fields from healthcare to robotics. One promising area is robotics, where the integration of OI could lead to the creation of more intelligent and adaptable machines. As robots become an integral part of our lives, enhancing their capabilities through OI could significantly transform industries such as manufacturing and transportation.
Another area poised for transformation is virtual assistance. Current virtual assistants, such as Siri and Alexa, are limited by traditional AI frameworks. By incorporating OI, these systems could vastly improve their ability to comprehend and engage in natural language, fundamentally altering human-technology interactions.
Conclusion
Organoid intelligence represents a groundbreaking approach to artificial intelligence, relying on the cultivation of miniature brains to execute tasks. While the potential of OI is vast, it is accompanied by significant challenges, particularly concerning ethical issues related to the creation of conscious entities and the potential for misuse.
To fully harness the capabilities of OI, it is vital to establish regulatory frameworks that ensure ethical practices and beneficial applications. By addressing these challenges, we can unlock OI's potential to develop adaptable and intelligent systems that surpass traditional AI.
The first video, "Brain Organoids and Robotics / AI - Sanford Stem Cell Symposium," provides insights into the intersection of organoid technology and AI, discussing advancements and future prospects.
The second video features Thomas Hartung discussing "Organoid Intelligence: New Frontier in Biocomputing and Intelligence-in-a-dish," exploring innovative applications and implications of organoid intelligence.